Government Revenue: The Backbone of Public Finance
Introduction: Government revenue is the financial foundation that enables governments to function and provide essential services to the public. It comprises all the income generated by the government through various means, primarily taxes, fees, and other financial instruments. The effective collection and management of government revenue are crucial for the economic stability and growth of a country. Without a steady stream of revenue, governments cannot fund infrastructure, social programs, defense, education, healthcare, or other public services.
Sources of Government Revenue:
- Taxes: Taxes are the most significant and consistent source of government revenue. They are compulsory financial charges imposed by governments on individuals, businesses, or transactions. Taxes are categorized into several types based on their nature:
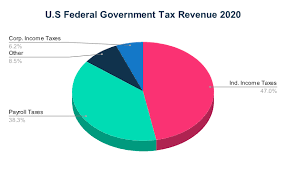
- Income Tax: This is levied on the income of individuals and corporations. Income tax is one of the primary sources of revenue in most countries. Progressive tax systems, where tax rates increase with income levels, are common in many countries.
- Corporate Tax: Companies are taxed on their profits, with rates varying depending on the jurisdiction. Corporate taxes play a major role in government revenue, especially in industrialized nations.
- Sales Tax/VAT (Value-Added Tax): Sales taxes are applied to goods and services purchased by consumers. VAT is a consumption tax placed on the value added to goods and services at each stage of production. Both sales tax and VAT are important revenue streams for many governments.
- Excise Tax: This tax is imposed on specific goods such as alcohol, tobacco, fuel, and luxury items. It is typically aimed at regulating consumption while generating revenue.
- Property Tax: This tax is levied on real estate properties, such as homes, commercial buildings, and land. Local governments often depend heavily on property taxes for funding public services, including education, fire, and police departments.
- Non-Tax Revenue: In addition to taxes, governments can generate revenue from various non-tax sources, which include:
- Fees and Charges: Governments charge fees for services they provide, such as licensing, tolls on roads, admission to parks or museums, and other public services. These fees help offset the costs of providing these services.
- Fines and Penalties: When individuals or businesses violate laws, they may face fines or penalties. These can include traffic fines, environmental violations, or business license penalties. Though not a regular source of income, fines contribute to government revenue.
- Profits from State-Owned Enterprises (SOEs): Many governments own and operate enterprises such as oil companies, utilities, or transportation networks. The profits from these businesses, in the form of dividends, are another significant source of non-tax revenue.
- Seigniorage: This is the revenue generated by the government from issuing currency. While this is not common in most modern economies, some governments still generate income from minting money, particularly in countries with large reserves of precious metals like gold.
- Borrowing (Public Debt): Although not a direct source of revenue in the traditional sense, governments may borrow funds to finance public expenditures. Borrowing allows governments to cover budget deficits or fund long-term infrastructure projects. This can be done by issuing government bonds, obtaining loans from international organizations, or borrowing from other countries. However, borrowing creates future liabilities and must be managed carefully to avoid fiscal instability.
Importance of Government Revenue:
- Funding Public Goods and Services: Government revenue ensures that the state can provide essential public goods and services such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, defense, and law enforcement. Without adequate revenue, these services cannot be delivered efficiently, which can harm economic growth and reduce the quality of life for citizens.
- Economic Stability and Growth: A stable flow of government revenue helps maintain economic stability by ensuring that the government can fund economic policies, subsidies, or stimulus programs during economic downturns. Revenue collection is also critical for managing inflation, controlling public debt, and addressing fiscal deficits.
- Redistribution of Wealth: Governments use revenue collection, particularly through taxes, to redistribute wealth in society. Progressive taxation (where wealthier individuals pay a higher percentage of their income) helps reduce income inequality. Government revenue can then be used to fund social welfare programs, such as unemployment benefits or public housing, aimed at supporting lower-income households.
- Addressing Externalities: Taxes and fees on specific goods, such as carbon taxes or tobacco taxes, can help address negative externalities. These taxes are designed to reduce harmful activities or behaviors and incentivize more sustainable practices, contributing to environmental protection and public health.
Challenges in Government Revenue Collection:
- Tax Evasion and Avoidance: Tax evasion (illegally avoiding tax payments) and tax avoidance (legally exploiting loopholes to minimize tax liabilities) are major issues in many countries. These practices can reduce government revenue and create inequities in the tax system. Governments must improve their tax enforcement systems to reduce these issues.
- Dependence on a Few Revenue Sources: Some countries heavily rely on a narrow range of revenue sources, such as oil exports or corporate taxes. This dependence can make governments vulnerable to economic shocks, such as fluctuations in global oil prices or economic recessions that affect corporate profitability.
- Inefficient Tax Systems: Inefficient and complex tax systems can make it difficult for businesses and individuals to comply with tax regulations. Simplifying tax codes and improving the efficiency of tax collection agencies can help increase revenue generation.
- Globalization and Digital Economy: Globalization and the rise of the digital economy present challenges for governments in collecting revenue. Many digital businesses operate across borders, making it difficult for governments to impose taxes effectively. International cooperation on tax policies and digital tax regulations is essential to address these issues.
Conclusion: Government revenue is the backbone of public finance, enabling governments to provide essential public services, invest in infrastructure, and maintain economic stability. While taxes remain the primary source of revenue, non-tax sources and borrowing also contribute significantly. Effective management of government revenue, including tackling challenges such as tax evasion and reliance on limited revenue sources, is critical for fostering sustainable development and ensuring equitable economic growth.
Leave a Reply